Definition of Liquidity of the Business in Accunting
What is Liquidity?
In financial markets Financial Markets Financial markets, from the name itself, are a type of marketplace that provides an avenue for the sale and purchase of assets such as bonds, stocks, foreign exchange, and derivatives. Often, they are called by different names, including "Wall Street" and "capital market," but all of them still mean one and the same thing. , liquidity refers to how quickly an investment can be sold without negatively impacting its price. The more liquid an investment is, the more quickly it can be sold (and vice versa), and the easier it is to sell it for fair value or current market value. All else being equal, more liquid assets trade at a premium Liquidity Premium A liquidity premium compensates investors for investing in securities with low liquidity. Liquidity refers to how easily an investment can be sold for cash. T-bills and stocks are considered to be highly liquid since they can usually be sold at any time at the prevailing market price. On the other hand, investments such as real estate or debt instruments and illiquid assets trade at a discount Discount Rate In corporate finance, a discount rate is the rate of return used to discount future cash flows back to their present value. This rate is often a company's Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC), required rate of return, or the hurdle rate that investors expect to earn relative to the risk of the investment. .
In accounting and financial analysis, a company's liquidity is a measure of how easily it can meet its short-term financial obligations Current Liabilities Current liabilities are financial obligations of a business entity that are due and payable within a year. A company shows these on the .
Ranking of Market Liquidity (Example)
Below is an example of how many common investments are typically ranked in terms how quickly and easily they can be turned into cash (of course, the order may be different depending on the circumstances).
Liquidity rankings:
- Cash
- Foreign Currency (FX FX Rates - Currencies The Table below has FX Rates for major Currencies, as compared to the USD. The USD is the most widely traded currency in the world, and is involved in over 81% of all forex trading. The USD is popularly referred to as the Greenback, due to its bill colour. )
- Guaranteed Investment Certificates (GICs)
- Government Bonds
- Corporate Bonds
- Stocks Common Stock Common stock is a type of security that represents ownership of equity in a company. There are other terms – such as common share, ordinary share, or voting share – that are equivalent to common stock. (publicly traded)
- Commodities (physical)
- Real Estate Real Estate Real estate is real property that consists of land and improvements, which include buildings, fixtures, roads, structures, and utility systems. Property rights give a title of ownership to the land, improvements, and natural resources such as minerals, plants, animals, water, etc.
- Art
- Private Businesses Private Company Valuation 3 techniques for Private Company Valuation - learn how to value a business even if it's private and with limited information. This guide provides examples including comparable company analysis, discounted cash flow analysis, and the first Chicago method. Learn how professionals value a business
As you can see in the list above, cash is, by default, the most liquid asset since it doesn't need to be sold or converted (it's already cash!). Stocks and bonds Bonds Bonds are fixed-income securities that are issued by corporations and governments to raise capital. The bond issuer borrows capital from the bondholder and makes fixed payments to them at a fixed (or variable) interest rate for a specified period. can typically be converted to cash in about 1-2 days, depending on the size of the investment. Finally, slower-to-sell investments such as real estate, art, and private businesses may take much longer to convert to cash (often months or even years).
Financial Liquidity
Items on a company's balance sheet are typically listed from the most to the least liquid. Therefore, cash is always listed at the top of the asset section, while other types of assets, such as Property, Plant & Equipment (PP&E), PP&E (Property, Plant and Equipment) PP&E (Property, Plant, and Equipment) is one of the core non-current assets found on the balance sheet. PP&E is impacted by Capex, are listed last.
In finance and accounting, the concept of a company's liquidity is its ability to meet its financial obligations. The most common measures of liquidity are:
- Current Ratio Current Ratio Formula The Current Ratio formula is = Current Assets / Current Liabilities. The current ratio, also known as the working capital ratio, measures the capability of a business to meet its short-term obligations that are due within a year. The ratio considers the weight of total current assets versus total current liabilities. It indicates the financial health of a company – Current assets minus current liabilities
- Quick Ratio Quick Ratio The Quick Ratio, also known as the Acid-test, measures the ability of a business to pay its short-term liabilities with assets readily convertible into cash – The ratio of only the most liquid assets (cash, accounts receivable, etc.) compared to current liabilities
- Cash Ratio Cash Ratio The cash ratio, sometimes referred to as the cash asset ratio, is a liquidity metric that indicates a company's capacity to pay off short-term debt obligations with its cash and cash equivalents. Compared to other liquidity ratios such as the current ratio and quick ratio, the cash ratio is a stricter, more conservative measure – Cash on hand relative to current liabilities
Liquidity Example (Balance Sheet)
Below is a screenshot of Amazon's 2017 balance sheet Balance Sheet The balance sheet is one of the three fundamental financial statements. The financial statements are key to both financial modeling and accounting. , which displays its assets and liabilities in order of their liquidity, as well as its stockholders' equity Stockholders Equity Stockholders Equity (also known as Shareholders Equity) is an account on a company's balance sheet that consists of share capital plus .
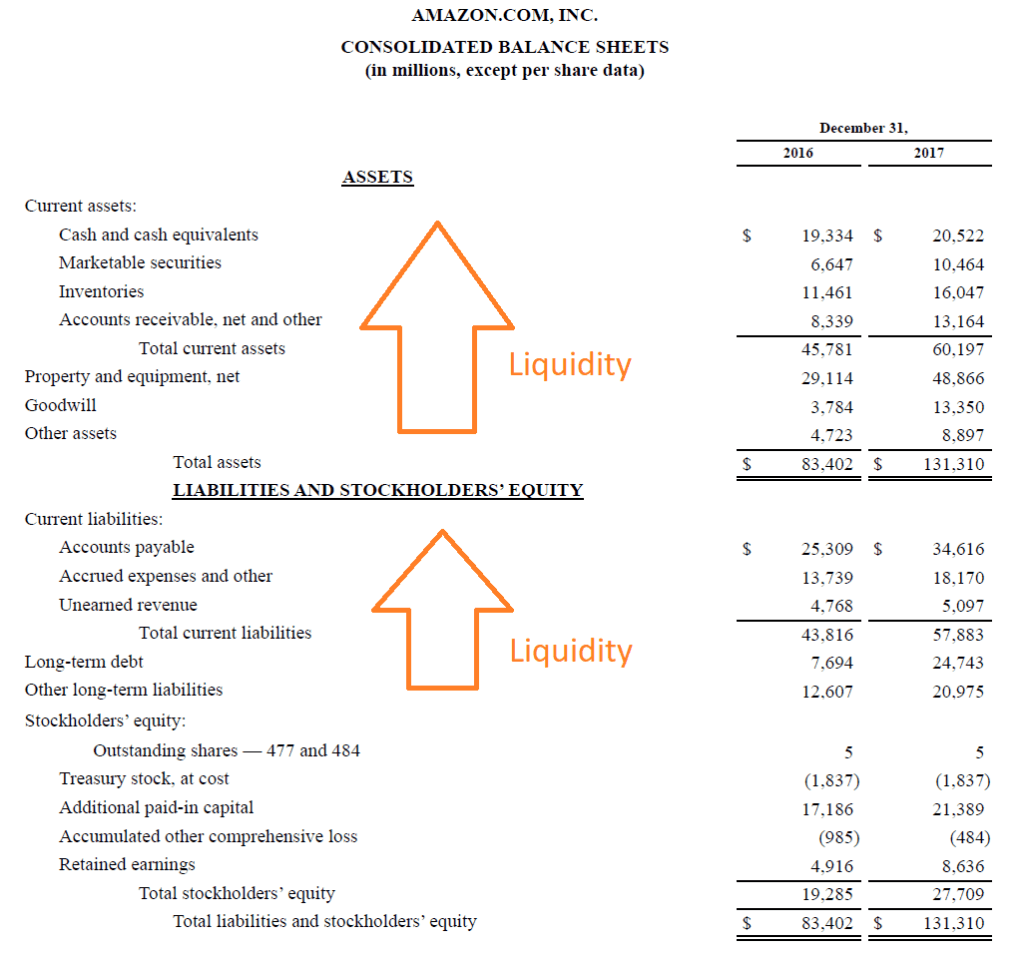
As you can see in the image, Amazon's assets are separated into two categories, current assets and non-current assets (everything else).
Current assets are as follows:
- Cash
- Marketable securities Marketable Securities Marketable securities are unrestricted short-term financial instruments that are issued either for equity securities or for debt securities of a publicly listed company. The issuing company creates these instruments for the express purpose of raising funds to further finance business activities and expansion. (These would include publicly traded stocks, bonds, and other investments)
- Inventories Inventory Inventory is a current asset account found on the balance sheet, consisting of all raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods that a (Products, finished goods, raw materials, etc. that can be sold)
- Accounts receivable Accounts Receivable Accounts Receivable (AR) represents the credit sales of a business, which have not yet been collected from its customers. Companies allow (Cash owed from sales to customers on credit)
For most companies, these are four of the most common current assets. Their liquidity, however, can vary. For many companies, accounts receivable is more liquid than inventories (meaning the company expects to receive payment from customers faster than it takes to sell products in inventory).
Current liabilities are listed as follows:
- Accounts payable Accounts Payable Accounts payable is a liability incurred when an organization receives goods or services from its suppliers on credit. Accounts payables are (money owed to vender and suppliers)
- Accrued expenses Accrued Expenses Accrued expenses are expenses that are recognized even though cash has not been paid. They are usually paired up against revenue via the matching principle and other (money the company expects to owe to vendors and suppliers in the near future)
- Unearned revenue (also called deferred revenue Deferred Revenue Deferred revenue is generated when a company receives payment for goods and/or services that it has not yet earned. In accrual accounting, )
To learn more, check out CFI's Advanced Financial Modeling Course on Amazon.
Additional Resources
CFI is the official provider of the global Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™ Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® CFI's Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today! certification program, designed to help anyone become a world-class financial analyst. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful:
- Current Assets Current Assets Current assets are all assets that a company expects to convert to cash within one year. They are commonly used to measure the liquidity of a
- Debt Capacity Debt Capacity Debt capacity refers to the total amount of debt a business can incur and repay according to the terms of the debt agreement.
- Idle Cash Idle Cash Idle cash is, as the phrase implies, cash that is idle or is not being used in a way that can increase the value of a business. It means that the cash is not earning interest from sitting in savings or a checking account, and is not generating a profit in the form of asset purchases or investments. The cash is simply sitting in a form where it does not appreciate.
- Types of Financial Ratios Financial Ratios Financial ratios are created with the use of numerical values taken from financial statements to gain meaningful information about a company
Definition of Liquidity of the Business in Accunting
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/finance/liquidity/
0 Response to "Definition of Liquidity of the Business in Accunting"
Postar um comentário